 |
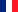
Dwarf Fox |
|
He is a wild animal |
Origin |
U.S.A. and Mexico | |
Translation |
Francis Vandersteen |
| The possession of this animal is not authorized Royal Decree establishing the list of mammals not kept for production purposes that may be kept (M.B. 24.08.2009) |
| The Dwarf Fox (Vulpes macrotis): Kit Fox, for Americans, is a fox belonging to the genus Vulpes and family Canidae. Endemic to North America, it is found in the southwestern United States and in northern and central Mexico. It is the smallest canid species on the continent. The northern limit of its range is the arid regions of Oregon, the eastern limit is southwestern Colorado, the southern limit is Nevada, Utah, southeastern California, Arizona, New Mexico and western Texas. The Dwarf Fox is the smallest species of the Canidae family found in North America. It has large ears, measuring between 71 and 95 mm, which help the fox to lower its body temperature and give it exceptional hearing (virtually identical to the fennec). This species is sexually dimorphic, with the male being considerably larger. The average weight of this species is between 1.5 and 2.7 kg. Body length is 455 to 535 mm. The tail is 250-340 mm longer. Its fur is usually gray, with rusty tones and a black tip on the tail. Unlike the gray fox, it has no stripes running the length of its tail. Its color ranges from yellowish to gray, and the back is usually darker than most of the rest of its fur, while its belly and the inside of its ears are generally lighter. It has distinct dark patches around the muzzle. The Dwarf Fox is essentially a nocturnal animal, but occasionally ventures out of its burrow during the day. It comes out to hunt shortly after sunset, eating mainly small animals such as kangaroo rats, cottontail rabbits, California hares (Lepus californicus), prairie voles, prairie dogs, insects, lizards, snakes, fish and ground-nesting birds. Although primitively carnivorous, if food runs short, it has been seen eating tomatoes, cactus fruit and other fruits. Different Dwarf Fox families may occupy the same hunting territory, but they don't usually hunt at the same times. Dwarf foxes prefer arid climates such as garrigue, chaparral and grassland. They can also be found in urban and agricultural areas. They are found at altitudes of 400 to 1,900 meters. Male and female kit foxes are monogamous and faithful, mating during October and November. Polygamy has been observed in pair relationships. Pairs may change from one year to the next. They mate from December to February, when family densities are higher. Parturition takes place in March and April, usually with 1 to 7 young, averaging 4. Gestation is 49 to 55 days. The young don't leave the den until they are 4 weeks old. They are weaned at 8 weeks and become independent between 5 and 6 months. They are sexually mature at 10 months. Both parents take part in raising and protecting their offspring. The average lifespan of a wild kit fox in the wild is 5.5 years. In captivity, they can live up to 12 years. A Californian study of 144 young kit foxes showed a 74% mortality rate in the first year. |





 English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)