 |
Berger Himalayen |
|
He is not recognized by the F.C.I. |
Origin |
Tibet | |
Translation |
Francis Vandersteen | |
This breed is also known as |
Himalayan Sheep Dog
|
Brief historical summary |
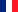
| Intermediate-sized, powerful dog with strong bones. Standing upright, he should look good, with his compact, robust body without being massive, and his beautiful bushy tail turned over. Reserved by nature. Wonderful shepherding and guarding instincts. Usually sleeps during the day and keeps watch at night. |
Head |
||
Cranial region |
||
Head |
Medium-sized, rather flat on top. | |
Stop |
Not very pronounced. | |
Facial region |
||
Nose |
Black. | |
Lips |
Full but tight. | |
Jaws and teeth |
Scissor bite, powerful jaw. | |
Eyes |
Not prominent, reddish-brown. | |
Ears |
Triangular shape, rounded tips, medium length, hanging ears, ears held high. | |
Body |
||
Body |
Powerful and compact. | |
Back |
Powerful, medium length. | |
Chest |
Deep and well sprung. | |
Tail |
| Thick, bushy and of medium length. |
Limbs |
Forequarters |
||
Generality |
Vertical. | |
Shoulders |
Sloping. | |
Pastern |
Slightly sloping. | |
Hindquarters |
||
Generality |
Powerful and well muscled. | |
Stifle |
Stifle angle sufficiently closed. | |
Hock |
Well let down. | |
Coat |
||
Hair |
Long and hard with thick undercoat. | |
Colour |
Black, Black and Tan, golden and cream; white patch on chest of a black or golden dog is permissible. A little white on the toes is permitted but not desirable. | |
Size and weight |
||
Height at withers |
53 to 61 cm for males and 46 to 58 cm for females. | |
Weight |
30 to 35 kg for the male and 25 to 30 kg for the female. | |
Faults |
| • Any departure from the foregoing points should be considered a fault and the seriousness with which the fault should be regarded should be in exact proportion to its degree and its effect upon the health and welfare of the dog and its ability to perform its traditional work. • Faults listed should be in degree of seriousness. |
NB : |
| • Any dog clearly showing physical or behavioural abnormalities shall be disqualified. • The above mentioned faults when occurring to a highly marked degree or frequently are disqualifying. • Male animals should have two apparently normal testicles fully descended into the scrotum. • Only functionally and clinically healthy dogs, with breed typical conformation should be used for breeding. |





 English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)